Q1: What do you know about Java?
A: Java is nothing but a high-level programming language from the Sun Microsystem. It is released in the year 1995 and runs on multiple platforms like Windows, Mac and other variations of UNIX.
Q2: Can you differentiate between J2SDK 1.5 and J2SDK 5.0?
There is no difference between J2SDK 1.5 and J2SDK 5.0. Sun Microsystems has just rebranded the versions.
Q3: Can you name a few platforms that support Java?
A: Yes, Java is supported by Windows, Mac as well as UNIX/Linux like Ubuntu, Red Hat and Sun Solaris.
Q4: Could you tell me why Java is called Architectural Neutral?
A: The main reason is because the compiler creates an architecture-natural object file format. This makes the compiled code to be executable on different other processors.
Q5: Could you differentiate an Interface and an Abstract class?
A: An abstract class may have instance methods, which can implement a default behavior. On the other hand, an interface can’t implement any default behavior. However, it can declare different constants and instance methods. While an interface has all the public members, an abstract class contains only class members like private, protected and so on.
Q6: What are the different ways you can use “Static”?
A: Static can be used in four ways: static variables, static methods, static classes and it can be used across a block of code in any class in order to indicate code that runs when a virtual machine starts and before the instances are created.
Q7: Do you think all property of Immutable Object needs to be final?
A: Not compulsory as we can easily achieve the same by making member as non-final but private and not changing them except in the constructor. Also, avoid providing setter methods for them. If it is a mutable object, then prevent leaking any reference for that member.
Q8: Can you brief me about Singleton Class?
A: It basically controls object creation, restricting the number to one while allowing the flexibility to create objects if the scenario changes.
Q9: In Java, what is the default value of Float and Double?
A: Default value of Float is 0.0f while 0.0d for Double.
Q10: Can you explain Type Erasure?
A: It is nothing but a JVM phenomenon, which means that the runtime has no idea about the types of generic objects like List<Integer>.
Q11: Explain Dot Operator.
A: It is used to access the instance variables and methods of class objects. Also, we can use it to access classes and sub-packages from a package.
Q12: What do you mean by Serialization in Java?
A: Well, serialization is nothing but a process of transforming objects into a stream of bytes.
Q13: Can you tell me the reason why String class is considered immutable?
A: It is because to avoid change in String object once it is created. As String is immutable, you can share it between different threads in a safe way. This is quite crucial in multithreaded programming.
Q14: Can you quickly brief about Map, HashMap, HashTable, and TreeMap?
A: Map is an interface
HashMap is a class that implements a Map. It is unsynchronized and supports null values and keys
Hashtable is a synchronized version of HashMap
TreeMap is similar to HashMap but uses Tree to implement Map
Q15: Do you think not overriding hashcode() method has any performance implication?
A: A weak hashcode function will result into frequent collision in HashMap, which will at the end increase the time to add an object within Hash Map.
Q16: Can you explain when and why Getters and Setters important?
A: We can put setters and getters within interfaces, which can hide implementation details. This allows us to make member variables public in Java.
Q17: Is it possible to import same package or class twice? Will the JVM load the package twice at runtime?
A: It is possible to import the same package or class more than one time. Also, it won’t have any effect on compiler or JVM. JVM will load the class for one time only, irrespective of the number of times you import the same class.
Q18: What is difference between Throw and Throws?
A: While Throw is used to trigger an exception, Throws is used in the declaration of exception. It is not possible to handle checked exception without Throws.
Q19: What is the significance of the order in which catch statements for FileNotFoundException and IOException are written?
A: It is crucial to consider the order as the FileNoFoundException is inherited from the IOException. Therefore, it is important that exception's subclasses caught first.
Q20: Can throw some light on Yielding and Sleeping?
A: When any task invokes its yield() method, it will return to the ready state. Whenever a task invokes sleep() method, it will return to the wait state.
Q21: Why you should use Vector class?
A: It provides the capability to implement a growable array of objects. It is quite useful when we don’t know the exact size of the array.
Q22: Can you tell me the number of bits used to represent Unicode, ASCII, UTF-16, and UTF-8 characters?
A: For Unicode 16 bits and ASCII needs 7 bits. However, ASCII is usually represented as 8 bits. UTF-8 presents characters through 8, 16 and 18 bit pattern. UTF-16 will require 16-bit and larger bit patterns.
Q23: What is Applets?
A: A small programs based on Java that can be transformed from one computer to another using the Applet Viewer or web browser.
Q24: What is the use of Locale?
A: Locale is an object containing geographical, cultural and political information which helps in using custom codes and conventions of specific country or region for writing applications in that language.
Q25: What is the use of Java Package?
A: Java Package is useful for organizing projects containing multiple modules and protecting them from unauthorized access.
Q26: While working in the JVM, do we need to import java.lang package?
A: No, by default it is loaded in the JVM
Q27: Can Applets communicate with each other?
A: Yes, they can communicate via shared static variables even if they belong to same of different classes.
Q28: Can a .java file support more than one java classes?
A: Yes, it can support more than one Java classes in a condition where one of them is a public class.
Q29: MAIN, NEXT, DELETE & EXIT, which of these is a keyword in Java?
A: None of these is a keyword in Java
Q30: How to handle errors while writing or accessing Stored Procedures?
A: Store Procedure itself returns the error codes if any but, incase if it fails to do so, we can resort to catching SQL Exception.
Q31: From ArrayList and LinkedList, which one helps to perform an indexed search in a list of objects?
A: ArrayList
Q32: What is the use of File Class?
A: It helps in accessing files and directories of a local system.
Q33: Does Java support Default arguments?
A: No, it does not support
Q34: Describe lifecycle of Applets?
A: Initialization, Starting, Stopping, Destroying & Painting
Q35: What is the method applied to load an image in Applet class?
A: It’s getImage
Although the list is long, it contains both simple and complex development specific questions. If you are a fresher, make sure your basic concepts are strong. If you are experienced, do not worry about the questions you cannot answer. Make sure whatever you answer, it comes out with confidence.
Q1: What do you know about Java?
A: Java is nothing but a high-level programming language from the Sun Microsystem. It is released in the year 1995 and runs on multiple platforms like Windows, Mac and other variations of UNIX.
Q2: Can you differentiate between J2SDK 1.5 and J2SDK 5.0?
There is no difference between J2SDK 1.5 and J2SDK 5.0. Sun Microsystems has just rebranded the versions.
Q3: Can you name a few platforms that support Java?
A: Yes, Java is supported by Windows, Mac as well as UNIX/Linux like Ubuntu, Red Hat and Sun Solaris.
Q4: Could you tell me why Java is called Architectural Neutral?
A: The main reason is because the compiler creates an architecture-natural object file format. This makes the compiled code to be executable on different other processors.
Q5: Could you differentiate an Interface and an Abstract class?
A: An abstract class may have instance methods, which can implement a default behavior. On the other hand, an interface can’t implement any default behavior. However, it can declare different constants and instance methods. While an interface has all the public members, an abstract class contains only class members like private, protected and so on.
Q6: What are the different ways you can use “Static”?
A: Static can be used in four ways: static variables, static methods, static classes and it can be used across a block of code in any class in order to indicate code that runs when a virtual machine starts and before the instances are created.
Q7: Do you think all property of Immutable Object needs to be final?
A: Not compulsory as we can easily achieve the same by making member as non-final but private and not changing them except in the constructor. Also, avoid providing setter methods for them. If it is a mutable object, then prevent leaking any reference for that member.
Q8: Can you brief me about Singleton Class?
A: It basically controls object creation, restricting the number to one while allowing the flexibility to create objects if the scenario changes.
Q9: In Java, what is the default value of Float and Double?
A: Default value of Float is 0.0f while 0.0d for Double.
Q10: Can you explain Type Erasure?
A: It is nothing but a JVM phenomenon, which means that the runtime has no idea about the types of generic objects like List<Integer>.
Q11: Explain Dot Operator.
A: It is used to access the instance variables and methods of class objects. Also, we can use it to access classes and sub-packages from a package.
Q12: What do you mean by Serialization in Java?
A: Well, serialization is nothing but a process of transforming objects into a stream of bytes.
Q13: Can you tell me the reason why String class is considered immutable?
A: It is because to avoid change in String object once it is created. As String is immutable, you can share it between different threads in a safe way. This is quite crucial in multithreaded programming.
Q14: Can you quickly brief about Map, HashMap, HashTable, and TreeMap?
A: Map is an interface
HashMap is a class that implements a Map. It is unsynchronized and supports null values and keys
Hashtable is a synchronized version of HashMap
TreeMap is similar to HashMap but uses Tree to implement Map
Q15: Do you think not overriding hashcode() method has any performance implication?
A: A weak hashcode function will result into frequent collision in HashMap, which will at the end increase the time to add an object within Hash Map.
Q16: Can you explain when and why Getters and Setters important?
A: We can put setters and getters within interfaces, which can hide implementation details. This allows us to make member variables public in Java.
Q17: Is it possible to import same package or class twice? Will the JVM load the package twice at runtime?
A: It is possible to import the same package or class more than one time. Also, it won’t have any effect on compiler or JVM. JVM will load the class for one time only, irrespective of the number of times you import the same class.
Q18: What is difference between Throw and Throws?
A: While Throw is used to trigger an exception, Throws is used in the declaration of exception. It is not possible to handle checked exception without Throws.
Q19: What is the significance of the order in which catch statements for FileNotFoundException and IOException are written?
A: It is crucial to consider the order as the FileNoFoundException is inherited from the IOException. Therefore, it is important that exception's subclasses caught first.
Q20: Can throw some light on Yielding and Sleeping?
A: When any task invokes its yield() method, it will return to the ready state. Whenever a task invokes sleep() method, it will return to the wait state.
Q21: Why you should use Vector class?
A: It provides the capability to implement a growable array of objects. It is quite useful when we don’t know the exact size of the array.
Q22: Can you tell me the number of bits used to represent Unicode, ASCII, UTF-16, and UTF-8 characters?
A: For Unicode 16 bits and ASCII needs 7 bits. However, ASCII is usually represented as 8 bits. UTF-8 presents characters through 8, 16 and 18 bit pattern. UTF-16 will require 16-bit and larger bit patterns.
Q23: What is Applets?
A: A small programs based on Java that can be transformed from one computer to another using the Applet Viewer or web browser.
Q24: What is the use of Locale?
A: Locale is an object containing geographical, cultural and political information which helps in using custom codes and conventions of specific country or region for writing applications in that language.
Q25: What is the use of Java Package?
A: Java Package is useful for organizing projects containing multiple modules and protecting them from unauthorized access.
Q26: While working in the JVM, do we need to import java.lang package?
A: No, by default it is loaded in the JVM
Q27: Can Applets communicate with each other?
A: Yes, they can communicate via shared static variables even if they belong to same of different classes.
Q28: Can a .java file support more than one java classes?
A: Yes, it can support more than one Java classes in a condition where one of them is a public class.
Q29: MAIN, NEXT, DELETE & EXIT, which of these is a keyword in Java?
A: None of these is a keyword in Java
Q30: How to handle errors while writing or accessing Stored Procedures?
A: Store Procedure itself returns the error codes if any but, incase if it fails to do so, we can resort to catching SQL Exception.
Q31: From ArrayList and LinkedList, which one helps to perform an indexed search in a list of objects?
A: ArrayList
Q32: What is the use of File Class?
A: It helps in accessing files and directories of a local system.
Q33: Does Java support Default arguments?
A: No, it does not support
Q34: Describe lifecycle of Applets?
A: Initialization, Starting, Stopping, Destroying & Painting
Q35: What is the method applied to load an image in Applet class?
A: It’s getImage
Although the list is long, it contains both simple and complex development specific questions. If you are a fresher, make sure your basic concepts are strong. If you are experienced, do not worry about the questions you cannot answer. Make sure whatever you answer, it comes out with confidence.
Q1: What do you know about Java?
A: Java is nothing but a high-level programming language from the Sun Microsystem. It is released in the year 1995 and runs on multiple platforms like Windows, Mac and other variations of UNIX.
Q2: Can you differentiate between J2SDK 1.5 and J2SDK 5.0?
There is no difference between J2SDK 1.5 and J2SDK 5.0. Sun Microsystems has just rebranded the versions.
Q3: Can you name a few platforms that support Java?
A: Yes, Java is supported by Windows, Mac as well as UNIX/Linux like Ubuntu, Red Hat and Sun Solaris.
Q4: Could you tell me why Java is called Architectural Neutral?
A: The main reason is because the compiler creates an architecture-natural object file format. This makes the compiled code to be executable on different other processors.
Q5: Could you differentiate an Interface and an Abstract class?
A: An abstract class may have instance methods, which can implement a default behavior. On the other hand, an interface can’t implement any default behavior. However, it can declare different constants and instance methods. While an interface has all the public members, an abstract class contains only class members like private, protected and so on.
Q6: What are the different ways you can use “Static”?
A: Static can be used in four ways: static variables, static methods, static classes and it can be used across a block of code in any class in order to indicate code that runs when a virtual machine starts and before the instances are created.
Q7: Do you think all property of Immutable Object needs to be final?
A: Not compulsory as we can easily achieve the same by making member as non-final but private and not changing them except in the constructor. Also, avoid providing setter methods for them. If it is a mutable object, then prevent leaking any reference for that member.
Q8: Can you brief me about Singleton Class?
A: It basically controls object creation, restricting the number to one while allowing the flexibility to create objects if the scenario changes.
Q9: In Java, what is the default value of Float and Double?
A: Default value of Float is 0.0f while 0.0d for Double.
Q10: Can you explain Type Erasure?
A: It is nothing but a JVM phenomenon, which means that the runtime has no idea about the types of generic objects like List<Integer>.
Q11: Explain Dot Operator.
A: It is used to access the instance variables and methods of class objects. Also, we can use it to access classes and sub-packages from a package.
Q12: What do you mean by Serialization in Java?
A: Well, serialization is nothing but a process of transforming objects into a stream of bytes.
Q13: Can you tell me the reason why String class is considered immutable?
A: It is because to avoid change in String object once it is created. As String is immutable, you can share it between different threads in a safe way. This is quite crucial in multithreaded programming.
Q14: Can you quickly brief about Map, HashMap, HashTable, and TreeMap?
A: Map is an interface
HashMap is a class that implements a Map. It is unsynchronized and supports null values and keys
Hashtable is a synchronized version of HashMap
TreeMap is similar to HashMap but uses Tree to implement Map
Q15: Do you think not overriding hashcode() method has any performance implication?
A: A weak hashcode function will result into frequent collision in HashMap, which will at the end increase the time to add an object within Hash Map.
Q16: Can you explain when and why Getters and Setters important?
A: We can put setters and getters within interfaces, which can hide implementation details. This allows us to make member variables public in Java.
Q17: Is it possible to import same package or class twice? Will the JVM load the package twice at runtime?
A: It is possible to import the same package or class more than one time. Also, it won’t have any effect on compiler or JVM. JVM will load the class for one time only, irrespective of the number of times you import the same class.
Q18: What is difference between Throw and Throws?
A: While Throw is used to trigger an exception, Throws is used in the declaration of exception. It is not possible to handle checked exception without Throws.
Q19: What is the significance of the order in which catch statements for FileNotFoundException and IOException are written?
A: It is crucial to consider the order as the FileNoFoundException is inherited from the IOException. Therefore, it is important that exception's subclasses caught first.
Q20: Can throw some light on Yielding and Sleeping?
A: When any task invokes its yield() method, it will return to the ready state. Whenever a task invokes sleep() method, it will return to the wait state.
Q21: Why you should use Vector class?
A: It provides the capability to implement a growable array of objects. It is quite useful when we don’t know the exact size of the array.
Q22: Can you tell me the number of bits used to represent Unicode, ASCII, UTF-16, and UTF-8 characters?
A: For Unicode 16 bits and ASCII needs 7 bits. However, ASCII is usually represented as 8 bits. UTF-8 presents characters through 8, 16 and 18 bit pattern. UTF-16 will require 16-bit and larger bit patterns.
Q23: What is Applets?
A: A small programs based on Java that can be transformed from one computer to another using the Applet Viewer or web browser.
Q24: What is the use of Locale?
A: Locale is an object containing geographical, cultural and political information which helps in using custom codes and conventions of specific country or region for writing applications in that language.
Q25: What is the use of Java Package?
A: Java Package is useful for organizing projects containing multiple modules and protecting them from unauthorized access.
Q26: While working in the JVM, do we need to import java.lang package?
A: No, by default it is loaded in the JVM
Q27: Can Applets communicate with each other?
A: Yes, they can communicate via shared static variables even if they belong to same of different classes.
Q28: Can a .java file support more than one java classes?
A: Yes, it can support more than one Java classes in a condition where one of them is a public class.
Q29: MAIN, NEXT, DELETE & EXIT, which of these is a keyword in Java?
A: None of these is a keyword in Java
Q30: How to handle errors while writing or accessing Stored Procedures?
A: Store Procedure itself returns the error codes if any but, incase if it fails to do so, we can resort to catching SQL Exception.
Q31: From ArrayList and LinkedList, which one helps to perform an indexed search in a list of objects?
A: ArrayList
Q32: What is the use of File Class?
A: It helps in accessing files and directories of a local system.
Q33: Does Java support Default arguments?
A: No, it does not support
Q34: Describe lifecycle of Applets?
A: Initialization, Starting, Stopping, Destroying & Painting
Q35: What is the method applied to load an image in Applet class?
A: It’s getImage
Although the list is long, it contains both simple and complex development specific questions. If you are a fresher, make sure your basic concepts are strong. If you are experienced, do not worry about the questions you cannot answer. Make sure whatever you answer, it comes out with confidence.
1) What is Java?
Java is the high-level, object-oriented, robust, secure programming language, platform-independent, high performance, Multithreaded, and portable programming language. It was developed by James Gosling in June 1991. It can also be known as the platform as it provides its own JRE and API.
2) What are the differences between C++ and Java?
The differences between C++ and Java are given in the following table.
| Comparison Index | C++ | Java |
|---|---|---|
| Platform-independent | C++ is platform-dependent. | Java is platform-independent. |
| Mainly used for | C++ is mainly used for system programming. | Java is mainly used for application programming. It is widely used in window, web-based, enterprise and mobile applications. |
| Design Goal | C++ was designed for systems and applications programming. It was an extension of C programming language. | Java was designed and created as an interpreter for printing systems but later extended as a support network computing. It was designed with a goal of being easy to use and accessible to a broader audience. |
| Goto | C++ supports the goto statement. | Java doesn't support the goto statement. |
| Multiple inheritance | C++ supports multiple inheritance. | Java doesn't support multiple inheritance through class. It can be achieved by interfaces in java. |
| Operator Overloading | C++ supports operator overloading. | Java doesn't support operator overloading. |
| Pointers | C++ supports pointers. You can write pointer program in C++. | Java supports pointer internally. However, you can't write the pointer program in java. It means java has restricted pointer support in java. |
| Compiler and Interpreter | C++ uses compiler only. C++ is compiled and run using the compiler which converts source code into machine code so, C++ is platform dependent. | Java uses compiler and interpreter both. Java source code is converted into bytecode at compilation time. The interpreter executes this bytecode at runtime and produces output. Java is interpreted that is why it is platform independent. |
| Call by Value and Call by reference | C++ supports both call by value and call by reference. | Java supports call by value only. There is no call by reference in java. |
| Structure and Union | C++ supports structures and unions. | Java doesn't support structures and unions. |
| Thread Support | C++ doesn't have built-in support for threads. It relies on third-party libraries for thread support. | Java has built-in thread support. |
| Documentation comment | C++ doesn't support documentation comment. | Java supports documentation comment (/** ... */) to create documentation for java source code. |
| Virtual Keyword | C++ supports virtual keyword so that we can decide whether or not override a function. | Java has no virtual keyword. We can override all non-static methods by default. In other words, non-static methods are virtual by default. |
| unsigned right shift >>> | C++ doesn't support >>> operator. | Java supports unsigned right shift >>> operator that fills zero at the top for the negative numbers. For positive numbers, it works same like >> operator. |
| Inheritance Tree | C++ creates a new inheritance tree always. | Java uses a single inheritance tree always because all classes are the child of Object class in java. The object class is the root of the inheritance tree in java. |
| Hardware | C++ is nearer to hardware. | Java is not so interactive with hardware. |
| Object-oriented | C++ is an object-oriented language. However, in C language, single root hierarchy is not possible. | Java is also an object-oriented language. However, everything (except fundamental types) is an object in Java. It is a single root hierarchy as everything gets derived from java.lang.Object. |
3) List the features of Java Programming language.
There are the following features in Java Programming Language.
- Simple: Java is easy to learn. The syntax of Java is based on C++ which makes easier to write the program in it.
- Object-Oriented: Java follows the object-oriented paradigm which allows us to maintain our code as the combination of different type of objects that incorporates both data and behavior.
- Portable: Java supports read-once-write-anywhere approach. We can execute the Java program on every machine. Java program (.java) is converted to bytecode (.class) which can be easily run on every machine.
- Platform Independent: Java is a platform independent programming language. It is different from other programming languages like C and C++ which needs a platform to be executed. Java comes with its platform on which its code is executed. Java doesn't depend upon the operating system to be executed.
- Secured: Java is secured because it doesn't use explicit pointers. Java also provides the concept of ByteCode and Exception handling which makes it more secured.
- Robust: Java is a strong programming language as it uses strong memory management. The concepts like Automatic garbage collection, Exception handling, etc. make it more robust.
- Architecture Neutral: Java is architectural neutral as it is not dependent on the architecture. In C, the size of data types may vary according to the architecture (32 bit or 64 bit) which doesn't exist in Java.
- Interpreted: Java uses the Just-in-time (JIT) interpreter along with the compiler for the program execution.
- High Performance: Java is faster than other traditional interpreted programming languages because Java bytecode is "close" to native code. It is still a little bit slower than a compiled language (e.g., C++).
- Multithreaded: We can write Java programs that deal with many tasks at once by defining multiple threads. The main advantage of multi-threading is that it doesn't occupy memory for each thread. It shares a common memory area. Threads are important for multi-media, Web applications, etc.
- Distributed: Java is distributed because it facilitates users to create distributed applications in Java. RMI and EJB are used for creating distributed applications. This feature of Java makes us able to access files by calling the methods from any machine on the internet.
- Dynamic: Java is a dynamic language. It supports dynamic loading of classes. It means classes are loaded on demand. It also supports functions from its native languages, i.e., C and C++.
4) What do you understand by Java virtual machine?
Java Virtual Machine is a virtual machine that enables the computer to run the Java program. JVM acts like a run-time engine which calls the main method present in the Java code. JVM is the specification which must be implemented in the computer system. The Java code is compiled by JVM to be a Bytecode which is machine independent and close to the native code.
300 Core Java Interview Questions | Set 190% assurance of interview questionsThere is the list of 300 core java interview questions. If there is any core java interview question that has been asked to you, kindly post it in the ask question section. We assure that you will get here the 90% frequently asked interview questions and answers.The answers to the core java interview questions are short and to the point. The core java interview questions are categorized in Basics of java interview questions, OOPs interview questions, String Handling interview questions, Multithreading interview questions, collection interview questions, JDBC interview questions, etc. Core Java: Basics of Java Interview Questions1) What is Java?Java is the high-level, object-oriented, robust, secure programming language, platform-independent, high performance, Multithreaded, and portable programming language. It was developed by James Gosling in June 1991. It can also be known as the platform as it provides its own JRE and API.2) What are the differences between C++ and Java?The differences between C++ and Java are given in the following table.
3) List the features of Java Programming language.There are the following features in Java Programming Language.
4) What do you understand by Java virtual machine?Java Virtual Machine is a virtual machine that enables the computer to run the Java program. JVM acts like a run-time engine which calls the main method present in the Java code. JVM is the specification which must be implemented in the computer system. The Java code is compiled by JVM to be a Bytecode which is machine independent and close to the native code.5) What is the difference between JDK, JRE, and JVM?JVMJVM is an acronym for Java Virtual Machine; it is an abstract machine which provides the runtime environment in which Java bytecode can be executed. It is a specification which specifies the working of Java Virtual Machine. Its implementation has been provided by Oracle and other companies. Its implementation is known as JRE.JVMs are available for many hardware and software platforms (so JVM is platform dependent). It is a runtime instance which is created when we run the Java class. There are three notions of the JVM: specification, implementation, and instance. JREJRE stands for Java Runtime Environment. It is the implementation of JVM. The Java Runtime Environment is a set of software tools which are used for developing Java applications. It is used to provide the runtime environment. It is the implementation of JVM. It physically exists. It contains a set of libraries + other files that JVM uses at runtime.JDKJDK is an acronym for Java Development Kit. It is a software development environment which is used to develop Java applications and applets. It physically exists. It contains JRE + development tools. JDK is an implementation of any one of the below given Java Platforms released by Oracle Corporation:
6) How many types of memory areas are allocated by JVM?Many types:
7) What is JIT compiler?Just-In-Time(JIT) compiler: It is used to improve the performance. JIT compiles parts of the bytecode that have similar functionality at the same time, and hence reduces the amount of time needed for compilation. Here the term “compiler” refers to a translator from the instruction set of a Java virtual machine (JVM) to the instruction set of a specific CPU.8) What is the platform?A platform is the hardware or software environment in which a piece of software is executed. There are two types of platforms, software-based and hardware-based. Java provides the software-based platform.9) What are the main differences between the Java platform and other platforms?There are the following differences between the Java platform and other platforms.
10) What gives Java its 'write once and run anywhere' nature?The bytecode. Java compiler converts the Java programs into the class file (Byte Code) which is the intermediate language between source code and machine code. This bytecode is not platform specific and can be executed on any computer.11) What is classloader?Classloader is a subsystem of JVM which is used to load class files. Whenever we run the java program, it is loaded first by the classloader. There are three built-in classloaders in Java.
12) Is Empty .java file name a valid source file name?Yes, Java allows to save our java file by .java only, we need to compile it by javac .java and run by java classname Let's take a simple example:run it by java A 13) Is delete, next, main, exit or null keyword in java?No.14) If I don't provide any arguments on the command line, then what will the value stored in the String array passed into the main() method, empty or NULL?It is empty, but not null.15) What if I write static public void instead of public static void?The program compiles and runs correctly because the order of specifiers doesn't matter in Java.16) What is the default value of the local variables?The local variables are not initialized to any default value, neither primitives nor object references.17) What are the various access specifiers in Java?In Java, access specifiers are the keywords which are used to define the access scope of the method, class, or a variable. In Java, there are four access specifiers given below.
18) What is the purpose of static methods and variables?The methods or variables defined as static are shared among all the objects of the class. The static is the part of the class and not of the object. The static variables are stored in the class area, and we do not need to create the object to access such variables. Therefore, static is used in the case, where we need to define variables or methods which are common to all the objects of the class.For example, In the class simulating the collection of the students in a college, the name of the college is the common attribute to all the students. Therefore, the college name will be defined as static. 19) What are the advantages of Packages in Java?There are various advantages of defining packages in Java.
20) What is the output of the following Java program?30Javatpoint
Javatpoint1020
In the first case, 10 and 20 are treated as numbers and added to be 30. Now, their sum 30 is treated as the string and concatenated with the string Javatpoint. Therefore, the output will be 30Javatpoint. In the second case, the string Javatpoint is concatenated with 10 to be the string Javatpoint10 which will then be concatenated with 20 to be Javatpoint1020. 21) What is the output of the following Java program?200Javatpoint
Javatpoint200
In the first case, The numbers 10 and 20 will be multiplied first and then the result 200 is treated as the string and concatenated with the string Javatpoint to produce the output 200Javatpoint. In the second case, The numbers 10 and 20 will be multiplied first to be 200 because the precedence of the multiplication is higher than addition. The result 200 will be treated as the string and concatenated with the string Javatpointto produce the output as Javatpoint200. 22) What is the output of the following Java program?Core Java - OOPs Concepts: Initial OOPs Interview Questions23) What is object-oriented paradigm?It is a programming paradigm based on objects having data and methods defined in the class to which it belongs. Object-oriented paradigm aims to incorporate the advantages of modularity and reusability. Objects are the instances of classes which interacts with one another to design applications and programs. There are the following features of the object-oriented paradigm.
24) What is an object?The Object is the real-time entity having some state and behavior. In Java, Object is an instance of the class having the instance variables as the state of the object and the methods as the behavior of the object. The object of a class can be created by using the new keyword.25) What is the difference between an object-oriented programming language and object-based programming language?There are the following basic differences between the object-oriented language and object-based language.
26) What will be the initial value of an object reference which is defined as an instance variable?All object references are initialized to null in Java.Core Java - OOPs Concepts: Constructor Interview Questions27) What is the constructor?The constructor can be defined as the special type of method that is used to initialize the state of an object. It is invoked when the class is instantiated, and the memory is allocated for the object. Every time, an object is created using the new keyword, the default constructor of the class is called. The name of the constructor must be similar to the class name. The constructor must not have an explicit return type.More Details. 28) How many types of constructors are used in Java?Based on the parameters passed in the constructors, there are two types of constructors in Java.
 29) What is the purpose of a default constructor?The purpose of the default constructor is to assign the default value to the objects. The java compiler creates a default constructor implicitly if there is no constructor in the class.0 null
0 null
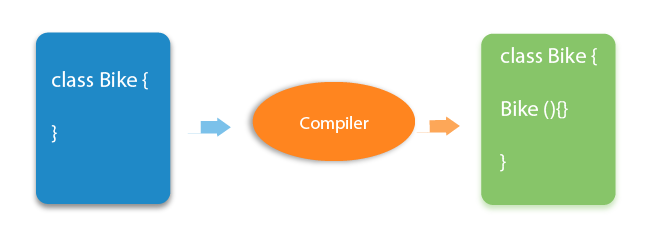 More Details. 30) Does constructor return any value?Ans: yes, The constructor implicitly returns the current instance of the class (You can't use an explicit return type with the constructor). More Details.31)Is constructor inherited?No, The constructor is not inherited.32) Can you make a constructor final?No, the constructor can't be final.33) Can we overload the constructors?Yes, the constructors can be overloaded by changing the number of arguments accepted by the constructor or by changing the data type of the parameters. Consider the following example.34) What do you understand by copy constructor in Java?There is no copy constructor in java. However, we can copy the values from one object to another like copy constructor in C++.There are many ways to copy the values of one object into another in java. They are:
111 Karan
111 Karan
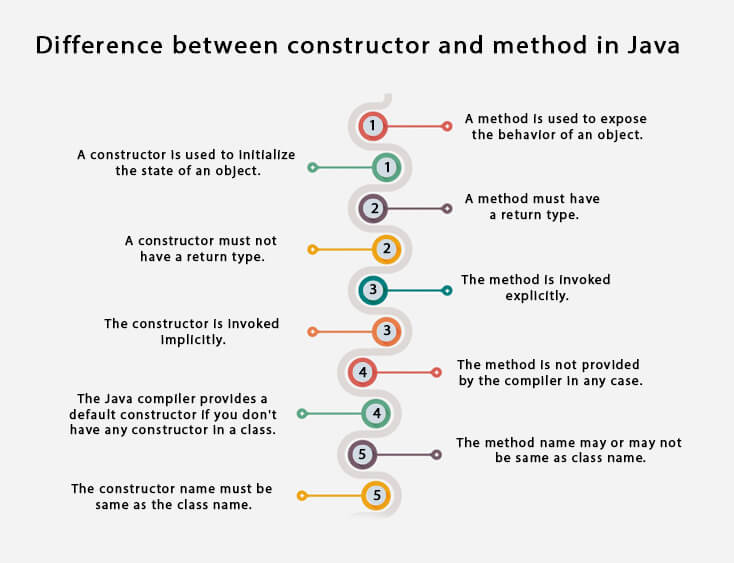
35) What are the differences between the constructors and methods?There are many differences between constructors and methods. They are given below.
 36) What is the output of the following Java program?a = 10 b = 15
37) What is the output of the following Java program?38) What is the output of the following Java program?Core Java - OOPs Concepts: static keyword Interview Questions39) What is the static variable?The static variable is used to refer to the common property of all objects (that is not unique for each object), e.g., The company name of employees, college name of students, etc. Static variable gets memory only once in the class area at the time of class loading. Using a static variable makes your program more memory efficient (it saves memory). Static variable belongs to the class rather than the object.Output:111 Karan ITS
222 Aryan ITS
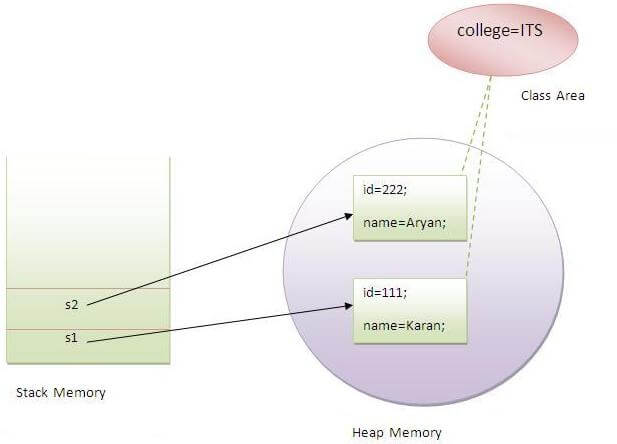 More Details. 40) What is the static method?
41) What are the restrictions that are applied to the Java static methods?Two main restrictions are applied to the static methods.
42) Why is the main method static?Because the object is not required to call the static method. If we make the main method non-static, JVM will have to create its object first and then call main() method which will lead to the extra memory allocation. More Details.43) Can we override the static methods?No, we can't override static methods.44) What is the static block?Static block is used to initialize the static data member. It is executed before the main method, at the time of classloading.Output: static block is invoked
Hello main
More Details. 45) Can we execute a program without main() method?Ans) Yes, one of the ways to execute the program without the main method is using static block. More Details.46) What if the static modifier is removed from the signature of the main method?Program compiles. However, at runtime, It throws an error "NoSuchMethodError."47) What is the difference between static (class) method and instance method?
48) Can we make constructors static?As we know that the static context (method, block, or variable) belongs to the class, not the object. Since Constructors are invoked only when the object is created, there is no sense to make the constructors static. However, if you try to do so, the compiler will show the compiler error.49) Can we make the abstract methods static in Java?In Java, if we make the abstract methods static, It will become the part of the class, and we can directly call it which is unnecessary. Calling an undefined method is completely useless therefore it is not allowed.50) Can we declare the static variables and methods in an abstract class?Yes, we can declare static variables and methods in an abstract method. As we know that there is no requirement to make the object to access the static context, therefore, we can access the static context declared inside the abstract class by using the name of the abstract class. Consider the following example.hi !! I am good !!
i = 102
Core Java - OOPs Concepts: Inheritance Interview Questions51) What is this keyword in java?The this keyword is a reference variable that refers to the current object. There are the various uses of this keyword in Java. It can be used to refer to current class properties such as instance methods, variable, constructors, etc. It can also be passed as an argument into the methods or constructors. It can also be returned from the method as the current class instance.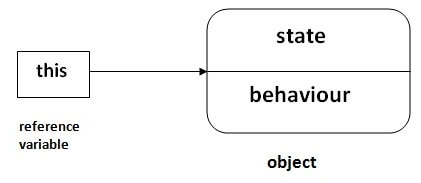 More Details. 52) What are the main uses of this keyword?There are the following uses of this keyword.
53) Can we assign the reference to this variable?No, this cannot be assigned to any value because it always points to the current class object and this is the final reference in Java. However, if we try to do so, the compiler error will be shown. Consider the following example.Test.java:5: error: cannot assign a value to final variable this
this = null;
^
1 error
54) Can this keyword be used to refer static members?Yes, It is possible to use this keyword to refer static members because this is just a reference variable which refers to the current class object. However, as we know that, it is unnecessary to access static variables through objects, therefore, it is not the best practice to use this to refer static members. Consider the following example.10
55) How can constructor chaining be done using this keyword?Constructor chaining enables us to call one constructor from another constructor of the class with respect to the current class object. We can use this keyword to perform constructor chaining within the same class. Consider the following example which illustrates how can we use this keyword to achieve constructor chaining.ID: 105 Name:Vikas age:22 address: Delhi
56) What are the advantages of passing this into a method instead of the current class object itself?As we know, that this refers to the current class object, therefore, it must be similar to the current class object. However, there can be two main advantages of passing this into a method instead of the current class object.
57) What is the Inheritance?Inheritance is a mechanism by which one object acquires all the properties and behavior of another object of another class. It is used for Code Reusability and Method Overriding. The idea behind inheritance in Java is that you can create new classes that are built upon existing classes. When you inherit from an existing class, you can reuse methods and fields of the parent class. Moreover, you can add new methods and fields in your current class also. Inheritance represents the IS-A relationship which is also known as a parent-child relationship.There are five types of inheritance in Java.
More Details. 58) Why is Inheritance used in Java?There are various advantages of using inheritance in Java that is given below.
59) Which class is the superclass for all the classes?The object class is the superclass of all other classes in Java.60) Why is multiple inheritance not supported in java?To reduce the complexity and simplify the language, multiple inheritance is not supported in java. Consider a scenario where A, B, and C are three classes. The C class inherits A and B classes. If A and B classes have the same method and you call it from child class object, there will be ambiguity to call the method of A or B class.Since the compile-time errors are better than runtime errors, Java renders compile-time error if you inherit 2 classes. So whether you have the same method or different, there will be a compile time error. Test it Now Compile Time Error
61) What is aggregation?Aggregation can be defined as the relationship between two classes where the aggregate class contains a reference to the class it owns. Aggregation is best described as a has-a relationship. For example, The aggregate class Employee having various fields such as age, name, and salary also contains an object of Address class having various fields such as Address-Line 1, City, State, and pin-code. In other words, we can say that Employee (class) has an object of Address class. Consider the following example.Address.java 111 varun
gzb UP india
112 arun
gno UP india
62) What is composition?Holding the reference of a class within some other class is known as composition. When an object contains the other object, if the contained object cannot exist without the existence of container object, then it is called composition. In other words, we can say that composition is the particular case of aggregation which represents a stronger relationship between two objects. Example: A class contains students. A student cannot exist without a class. There exists composition between class and students.63) What is the difference between aggregation and composition?Aggregation represents the weak relationship whereas composition represents the strong relationship. For example, the bike has an indicator (aggregation), but the bike has an engine (composition).64) Why does Java not support pointers?The pointer is a variable that refers to the memory address. They are not used in Java because they are unsafe(unsecured) and complex to understand.65) What is super in java?The super keyword in Java is a reference variable that is used to refer to the immediate parent class object. Whenever you create the instance of the subclass, an instance of the parent class is created implicitly which is referred by super reference variable. The super() is called in the class constructor implicitly by the compiler if there is no super or this.animal is created
dog is created
66) How can constructor chaining be done by using the super keyword?Name: Mukesh Salary: 90000.0 Age: 22 Address: Delhi
67) What are the main uses of the super keyword?There are the following uses of super keyword.
68) What are the differences between this and super keyword?There are the following differences between this and super keyword.
69) What is the output of the following Java program?Person class constructor called
Employee class constructor called
The super() is implicitly invoked by the compiler if no super() or this() is included explicitly within the derived class constructor. Therefore, in this case, The Person class constructor is called first and then the Employee class constructor is called. 70) Can you use this() and super() both in a constructor?No, because this() and super() must be the first statement in the class constructor.Example: Test.java:5: error: call to this must be first statement in constructor
71)What is object cloning?The object cloning is used to create the exact copy of an object. The clone() method of the Object class is used to clone an object. The java.lang.Cloneable interface must be implemented by the class whose object clone we want to create. If we don't implement Cloneable interface, clone() method generates CloneNotSupportedException.Core Java - OOPs Concepts: Method Overloading Interview Questions72) What is method overloading?Method overloading is the polymorphism technique which allows us to create multiple methods with the same name but different signature. We can achieve method overloading in two ways.
More Details. 73) Why is method overloading not possible by changing the return type in java?In Java, method overloading is not possible by changing the return type of the program due to avoid the ambiguity.Compile Time Error: method add(int, int) is already defined in class Adder
74) Can we overload the methods by making them static?No, We cannot overload the methods by just applying the static keyword to them(number of parameters and types are the same). Consider the following example.Animal.java:7: error: method consume(int) is already defined in class Animal
static void consume(int a)
^
Animal.java:15: error: non-static method consume(int) cannot be referenced from a static context
Animal.consume(20);
^
2 errors
75) Can we overload the main() method?Yes, we can have any number of main methods in a Java program by using method overloading.More Details. 76) What is method overloading with type promotion?By Type promotion is method overloading, we mean that one data type can be promoted to another implicitly if no exact matching is found.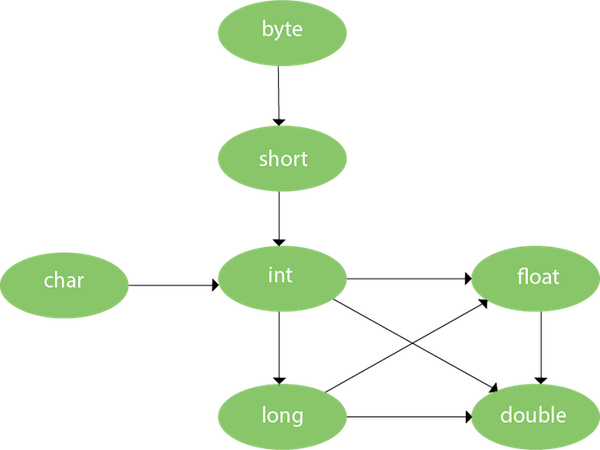 As displayed in the above diagram, the byte can be promoted to short, int, long, float or double. The short datatype can be promoted to int, long, float or double. The char datatype can be promoted to int, long, float or double and so on. Consider the following example. As displayed in the above diagram, the byte can be promoted to short, int, long, float or double. The short datatype can be promoted to int, long, float or double. The char datatype can be promoted to int, long, float or double and so on. Consider the following example.40
60
77) What is the output of the following Java program?OverloadingCalculation3.java:7: error: reference to sum is ambiguous
obj.sum(20,20);//now ambiguity
^
both method sum(int,long) in OverloadingCalculation3
and method sum(long,int) in OverloadingCalculation3 match
1 error
There are two methods defined with the same name, i.e., sum. The first method accepts the integer and long type whereas the second method accepts long and the integer type. The parameter passed that are a = 20, b = 20. We can not tell that which method will be called as there is no clear differentiation mentioned between integer literal and long literal. This is the case of ambiguity. Therefore, the compiler will throw an error. Core Java - OOPs Concepts: Method Overriding Interview Questions78) What is method overriding:If a subclass provides a specific implementation of a method that is already provided by its parent class, it is known as Method Overriding. It is used for runtime polymorphism and to implement the interface methods.Rules for Method overriding
79) Can we override the static method?No, you can't override the static method because they are the part of the class, not the object.80) Why can we not override static method?It is because the static method is the part of the class, and it is bound with class whereas instance method is bound with the object, and static gets memory in class area, and instance gets memory in a heap.81) Can we override the overloaded method?Yes.82) Difference between method Overloading and Overriding.
83) Can we override the private methods?No, we cannot override the private methods because the scope of private methods is limited to the class and we cannot access them outside of the class.84) Can we change the scope of the overridden method in the subclass?Yes, we can change the scope of the overridden method in the subclass. However, we must notice that we cannot decrease the accessibility of the method. The following point must be taken care of while changing the accessibility of the method.
85) Can we modify the throws clause of the superclass method while overriding it in the subclass?Yes, we can modify the throws clause of the superclass method while overriding it in the subclass. However, there are some rules which are to be followed while overriding in case of exception handling.
86) What is the output of the following Java program?Base class method called with integer a = 10
The method() is overloaded in class Base whereas it is derived in class Derived with the double type as the parameter. In the method call, the integer is passed. 87) Can you have virtual functions in Java?Yes, all functions in Java are virtual by default.88) What is covariant return type?Now, since java5, it is possible to override any method by changing the return type if the return type of the subclass overriding method is subclass type. It is known as covariant return type. The covariant return type specifies that the return type may vary in the same direction as the subclass.Output: welcome to covariant return type
89) What is the output of the following Java program?Output Derived method called ...
The method of Base class, i.e., baseMethod() is overridden in Derived class. In Test class, the reference variable b (of type Base class) refers to the instance of the Derived class. Here, Runtime polymorphism is achieved between class Base and Derived. At compile time, the presence of method baseMethod checked in Base class, If it presence then the program compiled otherwise the compiler error will be shown. In this case, baseMethod is present in Base class; therefore, it is compiled successfully. However, at runtime, It checks whether the baseMethod has been overridden by Derived class, if so then the Derived class method is called otherwise Base class method is called. In this case, the Derived class overrides the baseMethod; therefore, the Derived class method is called. Core Java - OOPs Concepts: final keyword Interview Questions90) What is the final variable?In Java, the final variable is used to restrict the user from updating it. If we initialize the final variable, we can't change its value. In other words, we can say that the final variable once assigned to a value, can never be changed after that. The final variable which is not assigned to any value can only be assigned through the class constructor. Output:Compile Time Error
91) What is the final method?If we change any method to a final method, we can't override it. More Details.Output:Compile Time Error
92) What is the final class?If we make any class final, we can't inherit it into any of the subclasses.Output:Compile Time Error
93) What is the final blank variable?A final variable, not initialized at the time of declaration, is known as the final blank variable. We can't initialize the final blank variable directly. Instead, we have to initialize it by using the class constructor. It is useful in the case when the user has some data which must not be changed by others, for example, PAN Number. Consider the following example:94) Can we initialize the final blank variable?Yes, if it is not static, we can initialize it in the constructor. If it is static blank final variable, it can be initialized only in the static block. More Details.95) Can you declare the main method as final?Yes, We can declare the main method as public static final void main(String[] args){}.96) What is the output of the following Java program?20
Since i is the blank final variable. It can be initialized only once. We have initialized it to 20. Therefore, 20 will be printed. 97) What is the output of the following Java program? Derived.java:11: error: getInfo() in Derived cannot override getInfo() in Base
protected final void getInfo()
^
overridden method is final
1 error
The getDetails() method is final; therefore it can not be overridden in the subclass. 98) Can we declare a constructor as final?The constructor can never be declared as final because it is never inherited. Constructors are not ordinary methods; therefore, there is no sense to declare constructors as final. However, if you try to do so, The compiler will throw an error.99) Can we declare an interface as final?No, we cannot declare an interface as final because the interface must be implemented by some class to provide its definition. Therefore, there is no sense to make an interface final. However, if you try to do so, the compiler will show an error.100) What is the difference between the final method and abstract method?The main difference between the final method and abstract method is that the abstract method cannot be final as we need to override them in the subclass to give its definition. |

 Download Android App
Download Android App


No comments:
Post a Comment